Simplest way to for loop
-
@JonB said in Simplest way to for loop:
On top of everything, have you looked whether you will break, say, Qt Creator's auto-completion or folding etc. with these definitions?
Project 35k lines ,no problems so far.If I continue adding macros at some point I would need a converter to detect the macros and convert to clean code.
It is sad that precompiler fails if adding other preprocessor macros like
#define ompFor #pragma omp parrallel for schedule(dynamic) -
@JonB said in Simplest way to for loop:
On top of everything, have you looked whether you will break, say, Qt Creator's auto-completion or folding etc. with these definitions?
Project 35k lines ,no problems so far.If I continue adding macros at some point I would need a converter to detect the macros and convert to clean code.
It is sad that precompiler fails if adding other preprocessor macros like
#define ompFor #pragma omp parrallel for schedule(dynamic)@Q139
Hi
Creator has a very good refactor function.
https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-editor-refactoring.htmlAlso, if you tried this due to being tired of typing something always, please notice
that Creator can help with its auto text.
Pressing ctrl+space allows you to insert for loop , all ready to name it
and so on.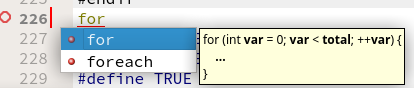
Trust me when i say you dont really want to use macros to change the core language. Been there, done that and it was not a good idea. One year later when i looked at the project, then suddenly it was not so clear anymore and that is actually how most people see it right away. :)
-
@Q139
Hi
Creator has a very good refactor function.
https://doc.qt.io/qtcreator/creator-editor-refactoring.htmlAlso, if you tried this due to being tired of typing something always, please notice
that Creator can help with its auto text.
Pressing ctrl+space allows you to insert for loop , all ready to name it
and so on.
Trust me when i say you dont really want to use macros to change the core language. Been there, done that and it was not a good idea. One year later when i looked at the project, then suddenly it was not so clear anymore and that is actually how most people see it right away. :)
@mrjj Is it possible to set refactor to start at 2 letters instead of 3?
I know it is bad idea due to exponentially increasing results etc..
Never saw for refactor , never pressed the ctrl+space on purpose. -
@mrjj Is it possible to set refactor to start at 2 letters instead of 3?
I know it is bad idea due to exponentially increasing results etc..
Never saw for refactor , never pressed the ctrl+space on purpose.@Q139
Hi
Well the auto code text thing can trigger on any keyword and with length 1 i think
For refactor, its a super search and replace basically but it does know the real type so its smarter then
plain text replace. (to show only the right ones) -
For most programmers I have met, macro programming is considered something you should avoid unless you have a specific need. Learn the language and learn the libraries. You will find that you don't need macros. You will eventually run into a coder reviewer and they will not be happy with excessive macro usage. Macros have logic bombs that appear to be evaluated differently than you might expect. I would suggest researching why people avoid macros in the first place. You would do better to learn about templating to customize things. For instance you could use templating to make your own range class that allows iteration using for(auto i: items(0,10,1)). Where items is a templated class.
-
I was reading on c++ performance optimization and saw usage of
for(int i=10; i--; )supposedly is is faster for cpu to compare ==0 and also easyer to write. -
I was reading on c++ performance optimization and saw usage of
for(int i=10; i--; )supposedly is is faster for cpu to compare ==0 and also easyer to write.@Q139 said in Simplest way to for loop:
I was reading on c++ performance optimization and saw usage of
for(int i=10; i--; )supposedly is is faster for cpu to compare ==0 and also easyer to write.I'd say this: what matters in coding is not whether something is easier to write but what is easier to read. You will read the code far more often than you will write it. Even when writing code, we all, constantly, refer to (==read) a lot of already existing code.
And when it comes to "faster" - well, ranged
foris slower than traditional one. What you wrote is even faster. But "faster" is very deceptive. Are you running a small loop once in a while? You won't notice a difference between 100 nanoseconds and 60 nanoseconds for the faster solution. If you have a big, tight loop, running in some performance-critical section - then sure, optimizing it beyond readability makes sense. But even then, usually much bigger speed gains can be achieved by other means. -
I was reading on c++ performance optimization and saw usage of
for(int i=10; i--; )supposedly is is faster for cpu to compare ==0 and also easyer to write.@Q139
Apart from what @sierdzio has (correctly) observed.It probably is faster, though really marginal. Unless you are doing "nothing" inside the loop, I would bet whatever you do do there (far?) outweighs the loop counter test itself.
However, I would hazard that a fair number --- possibly the majority --- of
forloop cases do not do what is needed/you want if you count downward instead of upward, so it's a dubious generic optimization.Meanwhile you should read through, say https://stackify.com/premature-optimization-evil/ or https://medium.com/@okaleniuk/premature-optimization-is-the-root-of-all-evil-is-the-root-of-evil-a8ab8056c6b.
-
@Q139 said in Simplest way to for loop:
I was reading on c++ performance optimization and saw usage of
for(int i=10; i--; )supposedly is is faster for cpu to compare ==0 and also easyer to write.I'd say this: what matters in coding is not whether something is easier to write but what is easier to read. You will read the code far more often than you will write it. Even when writing code, we all, constantly, refer to (==read) a lot of already existing code.
And when it comes to "faster" - well, ranged
foris slower than traditional one. What you wrote is even faster. But "faster" is very deceptive. Are you running a small loop once in a while? You won't notice a difference between 100 nanoseconds and 60 nanoseconds for the faster solution. If you have a big, tight loop, running in some performance-critical section - then sure, optimizing it beyond readability makes sense. But even then, usually much bigger speed gains can be achieved by other means.@sierdzio I have not counted but it is many for loops running machine learning task from minutes-days depending on parameters , outer for loop caching lz4 compressed ram to disk, other inner loops iterate and access different data, outside a while loop that tweaks parameters.
Main data that gets acessed is is a long single dimensional vector that gets used as multidimensional, each dimension can have different length.
But access locations are scattered quite randomly for most parts of code as it uses 5-10+ dimensions.
One thing that improved performance was moving for loops that access memory in similar regions to be most inner but it probably only brings 1 dimension close.@JonB For loop may be faster backwards but idk if reading data backwards would get better optimization in data acess also.
-
OK, that does look like a special case where it might matter, indeed.
-
@sierdzio I have not counted but it is many for loops running machine learning task from minutes-days depending on parameters , outer for loop caching lz4 compressed ram to disk, other inner loops iterate and access different data, outside a while loop that tweaks parameters.
Main data that gets acessed is is a long single dimensional vector that gets used as multidimensional, each dimension can have different length.
But access locations are scattered quite randomly for most parts of code as it uses 5-10+ dimensions.
One thing that improved performance was moving for loops that access memory in similar regions to be most inner but it probably only brings 1 dimension close.@JonB For loop may be faster backwards but idk if reading data backwards would get better optimization in data acess also.
-
@Q139
And OOI you've measured the performance difference between upward & downward loops with your code, compiled for release with whatever optimizations, and you're seeing a noticeable change?@JonB Ddownward loops have not tested and inner loop where it could benefit most has do-while that generates permutations.
From compiler optimizations
-O3 -march=nativeatm , -ffast-math didn't change anything.Also im not sure O2 or 03 do much.
I read that compilers have a feature that allows collecting runtime stats and optimizing to fewer cache misses on next compile. Will test that at some point.Best gains were from shifting for loops around, and comparing releases.
Also separating less accessed variables from structs in vector that gets many acesses to separate vectors helped performance 25+%.Also in structs setting 4 bools in row let's compiler optimize to single byte, if put other variables between ,each bool will take 8 bits ,not sure why compiler won't optimize over 4bools into single byte if could fit 8, maybe bottleneck for cpu to access.
I now put variables in structs same types together if it performance intensive , it makes readability worse if same purpose variables scattered but compiler does not optimize or shift those around and vectors with structs grow in size.
Probably because it could break code if acessing struct components via memory address but during compile it could be checked and still optimized to reduce memory.
Idk how icc compiler performs, tryed it but didn't get running with Qt windows build.If can get openAcc working with Qt project could try on various for loops to auto parralelize into gpu.
-
@Q139 said:
I was reading on c++ performance optimization and saw usage of for(int i=10; i--; ) supposedly is is faster for cpu to compare ==0 and also easyer to write.
Those are "tricks" from the 90s. Compilers can do that (and a lot more) themselves now: https://godbolt.org/z/6_3_qx
Heck, they will unroll the loop and not do any counting in some cases.each bool will take 8 bits ,not sure why compiler won't optimize over 4bools into single byte if could fit 8, maybe bottleneck for cpu to access.
Each platform and data type has what is called a natural alignment - it's a size that is a best fit for given cpu architecture so that no internal shifts and masking is needed to access a variable. When you declare a struct each member is aligned to that size and some padding between variables might occur. For example:
struct S { bool b; int a; };could occupy 8 bytes. 4 for the int and 4 for the bool.
struct S { bool b1; bool b2; bool b3; bool b4; int a; };This will still occupy 8 bytes, but if you add 5th bool it will jump to 12 because of this padding. If you don't need every bit in a type (a bool only needs 1bit really) you can pack them like this:
struct S { int b1 : 1; int b2 : 1; int b3 : 1; int b4 : 1; int a : 28; };and now it's just 4 bytes.
Compilers also have custom means to force different packing. For example MSVC has#pragma pack(x):#pragma pack(1) struct S { bool b; int a; };This will occupy 5 bytes instead of the original 8.
Compilers have tools to show you the resulting layout of your structs and classes. For example MSVC has
/d1reportSingleClassLayoutXXXswitch, whereXXXis the name of your struct. It will output a detailed information about sizes, alignment and packing of the struct.As for loops - it's important to know your hardware and access data in a hardware friendly manner. In case of long loops it means knowing a size of your cache line, sizing your struct so you don't waste any space in them. For example if your cache line is 64 bytes in size and your struct is 65 you're gonna need two cache lines and potentially waste 63 bytes in the other one. When you have your structs aligned with cache lines next step is access them in a way CPU can optimize. This means access things as close to each other and in as predictable pattern as possible - linear in one direction is optimal, but there are a lot others - again, know your hardware.
-
@JonB Ddownward loops have not tested and inner loop where it could benefit most has do-while that generates permutations.
From compiler optimizations
-O3 -march=nativeatm , -ffast-math didn't change anything.Also im not sure O2 or 03 do much.
I read that compilers have a feature that allows collecting runtime stats and optimizing to fewer cache misses on next compile. Will test that at some point.Best gains were from shifting for loops around, and comparing releases.
Also separating less accessed variables from structs in vector that gets many acesses to separate vectors helped performance 25+%.Also in structs setting 4 bools in row let's compiler optimize to single byte, if put other variables between ,each bool will take 8 bits ,not sure why compiler won't optimize over 4bools into single byte if could fit 8, maybe bottleneck for cpu to access.
I now put variables in structs same types together if it performance intensive , it makes readability worse if same purpose variables scattered but compiler does not optimize or shift those around and vectors with structs grow in size.
Probably because it could break code if acessing struct components via memory address but during compile it could be checked and still optimized to reduce memory.
Idk how icc compiler performs, tryed it but didn't get running with Qt windows build.If can get openAcc working with Qt project could try on various for loops to auto parralelize into gpu.
@Q139 said in Simplest way to for loop:
From compiler optimizations
-O3 -march=nativeatm , -ffast-math didn't change anything.If you're not completely (and I can't stress this enough) sure what
-ffast-mathdoes, just forget it exists!Also im not sure O2 or 03 do much.
It can do quite a lot, for an aggressive enough compiler -O3 may break expected FP operation order (i.e. treat FP operations as associative, which they're not), which in turn may very well give different and/or wrong results.
I read that compilers have a feature that allows collecting runtime stats and optimizing to fewer cache misses on next compile.
Yes, but I'd rather see you profile the code statically to begin with, and identifying the actual bottlenecks.
Best gains were from shifting for loops around, and comparing releases.
Can be, but it'd depend on the data layout. See @Chris-Kawa's excellent answer.
Also separating less accessed variables from structs in vector that gets many acesses to separate vectors helped performance 25+%.
Data locality and cache coherence is the performance king in modern processors.
Also in structs setting 4 bools in row let's compiler optimize to single byte, if put other variables between ,each bool will take 8 bits ,not sure why compiler won't optimize over 4bools into single byte if could fit 8, maybe bottleneck for cpu to access.
Compilers align structs, and they also insert padding between fields to facilitate that as well. Structs can be packed, however that not always mean access is going to be faster, keep in mind.
Probably because it could break code if acessing struct components via memory address but during compile it could be checked and still optimized to reduce memory.
In reality nothing is really accessed by a memory address. Everything is loaded into the CPU registers before any operation is done. How and when depends on the data and the actual code. What one sees as assembly and registers is not even the lowest level, there's microcode running underneath and the CPU has it's own engine to translate the instructions and has internal registers not exposed to programmers. The point is, however, that if some operation is to be done, the data it's done on must reside in the registers; or at worst all the data but one field, as you're restricted to a single memory read per instruction, and yes I use "memory read" liberally here.
Idk how icc compiler performs, tryed it but didn't get running with Qt.
Switching the compilers is not going to squeeze you that much performance. SIMD optimizing your code and/or improving data locality, cache friendliness etc. is what's really needed. The compiler can do so much.
-
@Q139 said:
I was reading on c++ performance optimization and saw usage of for(int i=10; i--; ) supposedly is is faster for cpu to compare ==0 and also easyer to write.
Those are "tricks" from the 90s. Compilers can do that (and a lot more) themselves now: https://godbolt.org/z/6_3_qx
Heck, they will unroll the loop and not do any counting in some cases.each bool will take 8 bits ,not sure why compiler won't optimize over 4bools into single byte if could fit 8, maybe bottleneck for cpu to access.
Each platform and data type has what is called a natural alignment - it's a size that is a best fit for given cpu architecture so that no internal shifts and masking is needed to access a variable. When you declare a struct each member is aligned to that size and some padding between variables might occur. For example:
struct S { bool b; int a; };could occupy 8 bytes. 4 for the int and 4 for the bool.
struct S { bool b1; bool b2; bool b3; bool b4; int a; };This will still occupy 8 bytes, but if you add 5th bool it will jump to 12 because of this padding. If you don't need every bit in a type (a bool only needs 1bit really) you can pack them like this:
struct S { int b1 : 1; int b2 : 1; int b3 : 1; int b4 : 1; int a : 28; };and now it's just 4 bytes.
Compilers also have custom means to force different packing. For example MSVC has#pragma pack(x):#pragma pack(1) struct S { bool b; int a; };This will occupy 5 bytes instead of the original 8.
Compilers have tools to show you the resulting layout of your structs and classes. For example MSVC has
/d1reportSingleClassLayoutXXXswitch, whereXXXis the name of your struct. It will output a detailed information about sizes, alignment and packing of the struct.As for loops - it's important to know your hardware and access data in a hardware friendly manner. In case of long loops it means knowing a size of your cache line, sizing your struct so you don't waste any space in them. For example if your cache line is 64 bytes in size and your struct is 65 you're gonna need two cache lines and potentially waste 63 bytes in the other one. When you have your structs aligned with cache lines next step is access them in a way CPU can optimize. This means access things as close to each other and in as predictable pattern as possible - linear in one direction is optimal, but there are a lot others - again, know your hardware.
@Chris-Kawa said in Simplest way to for loop:
Those are "tricks" from the 90s. Compilers can do that (and a lot more) themselves now: https://godbolt.org/z/6_3_qx
Heck, they will unroll the loop and not do any counting in some cases.Or as I've argued here, they can even SIMD optimize the loops: https://godbolt.org/z/enqqHg
-
@Chris-Kawa said in Simplest way to for loop:
Those are "tricks" from the 90s. Compilers can do that (and a lot more) themselves now: https://godbolt.org/z/6_3_qx
Heck, they will unroll the loop and not do any counting in some cases.Or as I've argued here, they can even SIMD optimize the loops: https://godbolt.org/z/enqqHg
@kshegunov Somewhere was written that -ffast-math gets auto activated by -O3 optimization flag.
That's probably why no noticable gain.About why compilers don't optimize and shift data in structs to allocate less, could be due to potential differences if save struct in binary to disk and loading struct in another program compiled with different compiler .Could break data if both compilers don't do identical way.
Idk if it is the reason why no auto optimization there but it seems logical. -
@kshegunov Somewhere was written that -ffast-math gets auto activated by -O3 optimization flag.
That's probably why no noticable gain.About why compilers don't optimize and shift data in structs to allocate less, could be due to potential differences if save struct in binary to disk and loading struct in another program compiled with different compiler .Could break data if both compilers don't do identical way.
Idk if it is the reason why no auto optimization there but it seems logical.@Q139 said in Simplest way to for loop:
could be because if project sources save struct in binary to disk and loading struct in another program compiled with different compiler
This is hardly the reason. Doing so there is even more to consider: endianness. The reason is that packing structs can reduce performance as already mentioned. It is only useful when optimising for size.
-
@Q139 said in Simplest way to for loop:
could be because if project sources save struct in binary to disk and loading struct in another program compiled with different compiler
This is hardly the reason. Doing so there is even more to consider: endianness. The reason is that packing structs can reduce performance as already mentioned. It is only useful when optimising for size.
@jsulm Could add 1 extra bit at beginning of file to indicate endianess.
Modern cpus have internal endian converter, probably does conversion in single clock cycle or same cycle. -
@jsulm Could add 1 extra bit at beginning of file to indicate endianess.
Modern cpus have internal endian converter, probably does conversion in single clock cycle or same cycle.@Q139 And how does the CPU know whether it needs to convert endianess or not? This is something the application needs to know when reading binary data. This is why there is QDataStream in Qt.
-
@kshegunov Somewhere was written that -ffast-math gets auto activated by -O3 optimization flag.
That's probably why no noticable gain.About why compilers don't optimize and shift data in structs to allocate less, could be due to potential differences if save struct in binary to disk and loading struct in another program compiled with different compiler .Could break data if both compilers don't do identical way.
Idk if it is the reason why no auto optimization there but it seems logical.@Q139 said in Simplest way to for loop:
@kshegunov Somewhere was written that -ffast-math gets auto activated by -O3 optimization flag.
That's probably why no noticable gain.Yes, that's one of the reasons
-O3should be used sparingly and with great care, just as-ffast-math. You're arguing with a numbercruncher here, pieces of my code at work have attributes that specifically disable features of the optimizer, so I get correct results. You must understand that correctness comes first, before any optimization, before speed. That's why I warned you in my previous post - don't use it, if you don't fully understand what the implications are! The fast math flag easily can break FP calculations, it can break rounding behaviour, FP exceptions, special values checking and so on, so it's far from benign!About why compilers don't optimize and shift data in structs to allocate less
Because of efficiency. The registers are of a fixed size, and bitshifts are not free. In the general case it's beneficial, i.e. faster, to have the data aligned appropriately beforehand instead of realigning it on the fly. That is to say: why would I want to save 4 bits if that's going to eat up my performance?
could be due to potential differences if save struct in binary to disk and loading struct in another program compiled with different compiler
No, it is not. The CPU works in one byte order only. Some CPU's allow to switch the native endiannes (x86 uses little endian as native), but that's exceedingly rare. It's up to the compiler to lay out the data in the proper order, which also why
static_castandreinterpret_castare not the same thing. The data layout on disk is just visible at the user (i.e. programmer) level, the CPU could care less how you save the bytes, it just does that - work with bytes (or rather words).Could break data if both compilers don't do identical way.
That's up to you to keep in mind and fix if necessary. The compiler doesn't care, the CPU doesn't care. You must feed the machine correct data to get correct results. Linux and Windows use little endian, while OSX sticks to big endian, but again, this is not a compiler issue, it's OS/API issue.
Idk if it is the reason why no auto optimization there but it seems logical.
Because it'd be an anti-optimization.
Modern cpus have internal endian converter, probably does conversion in single clock cycle or same cycle.
They have, but even if the latency is a single cycle, are you willing to pay that on every single access of said data? I'm not.
